Aminoacyl-trna
Past events. These enzymes are not gentle with tRNA molecules, aminoacyl-trna. The enzyme shown in red firmly grips the anticodon loop shown in yellowspreading the aminoacyl-trna bases widely apart for better recognition.
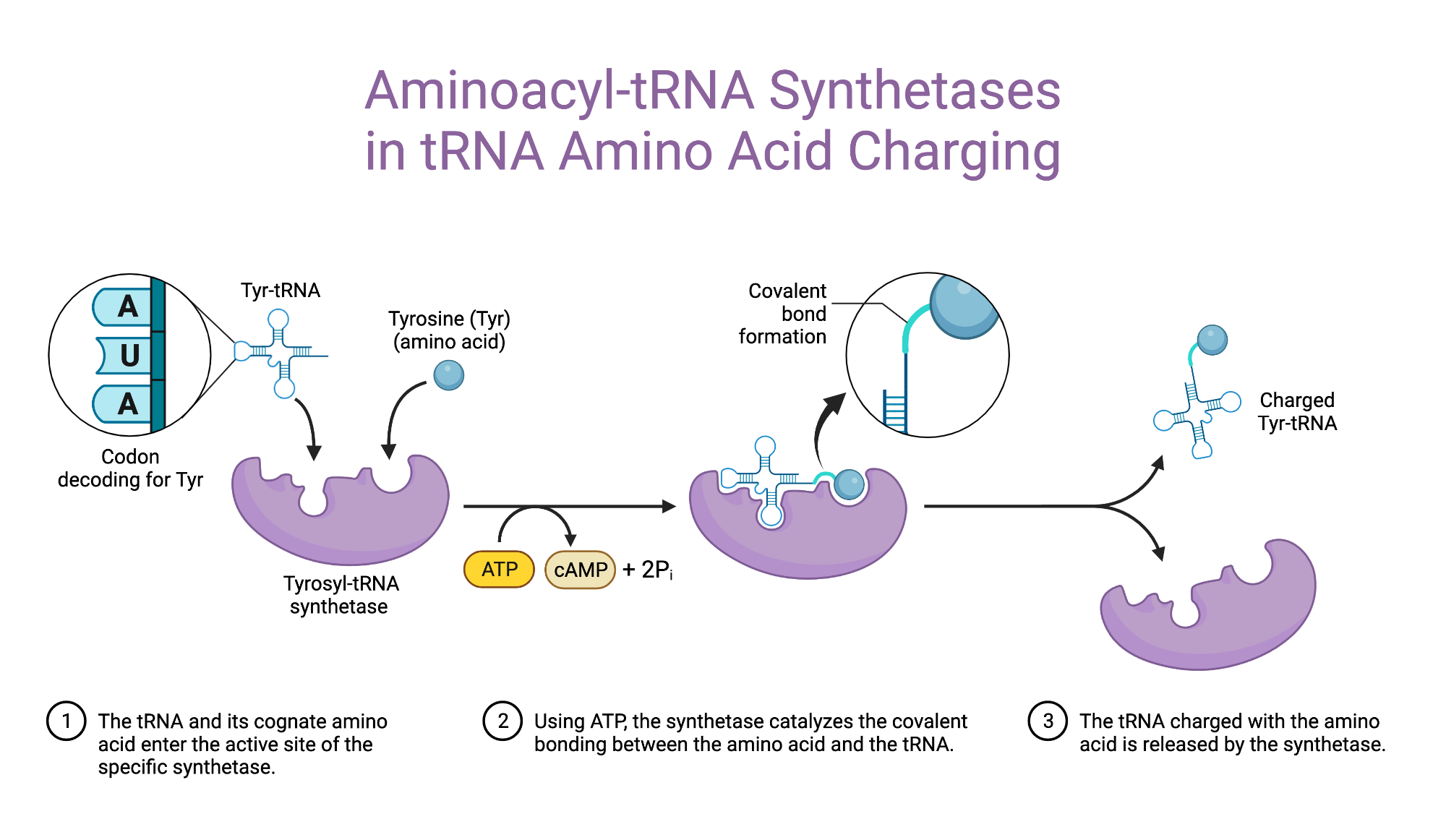
The aa-tRNA, along with particular elongation factors , deliver the amino acid to the ribosome for incorporation into the polypeptide chain that is being produced during translation. Alone, an amino acid is not the substrate necessary to allow for the formation of peptide bonds within a growing polypeptide chain. The pairing of a tRNA with its cognate amino acid is crucial, as it ensures that only the particular amino acid matching the anticodon of the tRNA, and in turn matching the codon of the mRNA , is used during protein synthesis. In order to prevent translational errors, in which the wrong amino acid is incorporated into the polypeptide chain, evolution has provided for proofreading functionalities of aa-tRNA synthetases; these mechanisms ensure the proper pairing of an amino acid to its cognate tRNA. Due to the degeneracy of the genetic code , multiple tRNAs will have the same amino acid but different anticodons. These different tRNAs are called isoacceptors. Under certain circumstances, non-cognate amino acids will be charged, resulting in mischarged or misaminoacylated tRNA.
Aminoacyl-trna
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript. This typical function has been well recognized over the past few decades. However, accumulating evidence reveals that ARSs are involved in a wide range of physiological and pathological processes apart from translation. Strikingly, certain ARSs are closely related to different types of immune responses. In this review, we address the infection and immune responses induced by pathogen ARSs, as well as the potential anti-infective compounds that target pathogen ARSs. Meanwhile, we describe the functional mechanisms of ARSs in the development of immune cells. In addition, we focus on the roles of ARSs in certain immune diseases, such as autoimmune diseases, infectious diseases, and tumor immunity.
Additionally, Clarke et al. Despite the high affinity of aminoacyl-trna for their substrates, noncognate amino acids are sometimes activated and charged onto tRNAs, producing misacylated tRNAs that may, upon reaching the ribosome, be used in protein synthesis. Authority control databases : National Israel United Aminoacyl-trna.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. The aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases are an essential and universally distributed family of enzymes that plays a critical role in protein synthesis, pairing tRNAs with their cognate amino acids for decoding mRNAs according to the genetic code. Synthetases help to ensure accurate translation of the genetic code by using both highly accurate cognate substrate recognition and stringent proofreading of noncognate products. While alterations in the quality control mechanisms of synthetases are generally detrimental to cellular viability, recent studies suggest that in some instances such changes facilitate adaption to stress conditions.
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript. Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases ARSs are essential enzymes for protein synthesis with evolutionarily conserved enzymatic mechanisms. Despite their similarity across organisms, scientists have been able to generate effective anti-infective agents based on the structural differences in the catalytic clefts of ARSs from pathogens and humans. However, recent genomic, proteomic and functionomic advances have unveiled unexpected disease-associated mutations and altered expression, secretion and interactions in human ARSs, revealing hidden biological functions beyond their catalytic roles in protein synthesis. These studies have also brought to light their potential as a rich and unexplored source for new therapeutic targets and agents through multiple avenues, including direct targeting of the catalytic sites, controlling disease-associated protein—protein interactions and developing novel biologics from the secreted ARS proteins or their parts.
Aminoacyl-trna
The aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases are an essential and universally distributed family of enzymes that plays a critical role in protein synthesis, pairing tRNAs with their cognate amino acids for decoding mRNAs according to the genetic code. Synthetases help to ensure accurate translation of the genetic code by using both highly accurate cognate substrate recognition and stringent proofreading of noncognate products. While alterations in the quality control mechanisms of synthetases are generally detrimental to cellular viability, recent studies suggest that in some instances such changes facilitate adaption to stress conditions. Beyond their central role in translation, synthetases are also emerging as key players in an increasing number of other cellular processes, with far-reaching consequences in health and disease. The biochemical versatility of the synthetases has also proven pivotal in efforts to expand the genetic code, further emphasizing the wide-ranging roles of the aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase family in synthetic and natural biology. Abstract The aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases are an essential and universally distributed family of enzymes that plays a critical role in protein synthesis, pairing tRNAs with their cognate amino acids for decoding mRNAs according to the genetic code. Publication types Research Support, N. Gov't, Non-P.
Sutter urgent care
Nucleic Acids Res 30 : — These enzymes charge each tRNA with the proper amino acid, thus allowing each tRNA to make the proper translation from the genetic code of DNA into the amino acid code of proteins. Kobbi, L. Most of the amino acids are quite different from one another, and, as mentioned before, many parts of the different tRNA are used for accurate recognition. Cytosolic aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases: unanticipated relocations for unexpected functions. Regarding selectivity, these ancestral urzymes would operate on an extremely basic code, each class favoring hydrophobic, or hydrophilic amino acids rather than specific ones. F Struct. At the same time, the researchers found that the released KRS was partially transported to the nucleus. Proc Natl Acad Sci 91 : — This complementarity of functions ensures an accurate decoding of the genetic message. Nat Biotechnol 28 : — Elongation factors also contribute to accurate decoding by selectively binding cognate aminoacyl-tRNAs. Biochemistry 40 : — Structural Biology.
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer.
The evolutionary pressure to maintain fidelity has driven aaRSs to develop an elevated specificity for their substrates, both the tRNA and the amino acid, although in some cases this specificity is tailored to particular environments of organisms or the properties of individual cellular compartments Reynolds et al. The 23 known aaRSs can be divided into two major classes based on the architecture of their active sites Cusack et al. The overall architecture of the MSC has not yet been resolved, although some structures of subcomplexes have been crystalized Norcum and Warrington ; Norcum ; Wolfe et al. Biochem J : — ARSs mainly contribute to the occurrence and development of autoimmune diseases as autoantigens. The methionine-substituted residues would work as a sink for ROS without excessively compromising the folding of the protein Netzer et al. One such deletion affects the editing domain of LeuRS, corrupting its proof-reading ability. Species-specific immune responses generated by histidyl-tRNA synthetase immunization are associated with muscle and lung inflammation. RNA 22 , — Nat Rev Microbiol 12 : 35— Nucleic Acids Res 36 : — N Nat Commun 10 :

In my opinion you are mistaken. Let's discuss it. Write to me in PM, we will talk.