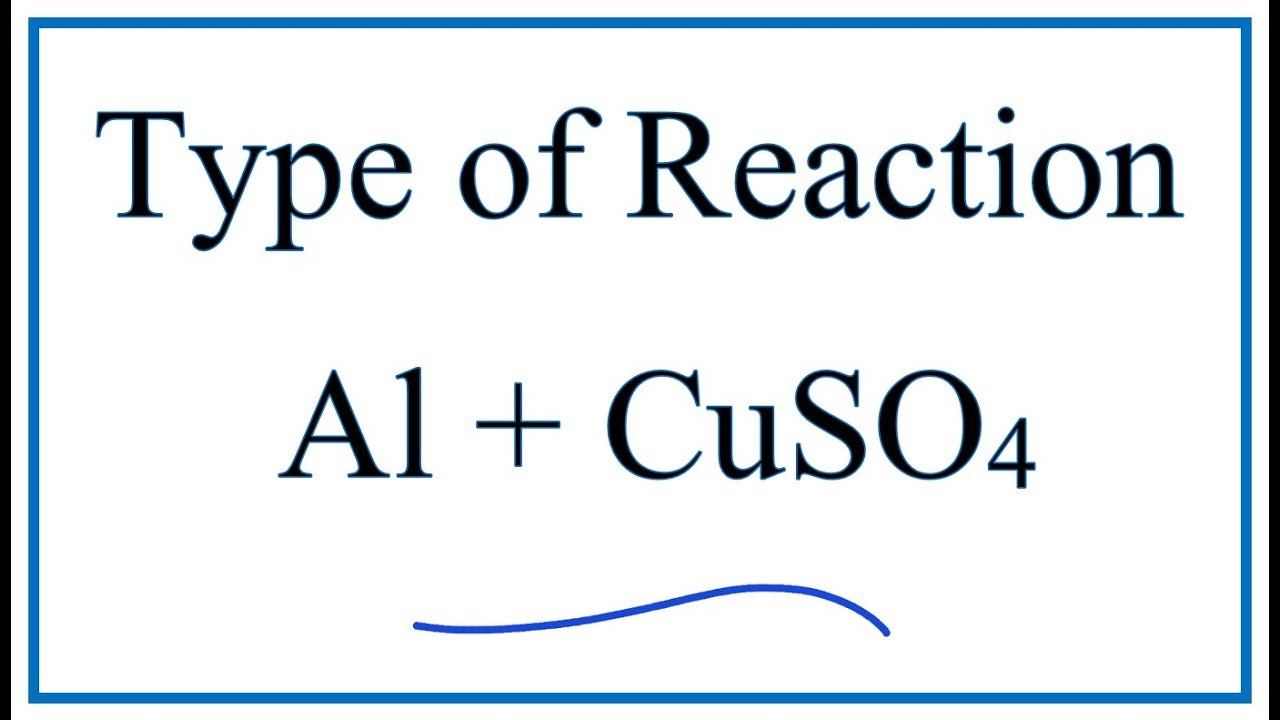
Al cuso4 reaction
Direct link to this balanced equation:, al cuso4 reaction. A chemical equation represents a chemical reaction. It shows the reactants substances that start a reaction and products substances formed by the reaction. However, this equation isn't balanced because the number of atoms for each element is not the same on both sides of the equation.
Direct link to this balanced equation:. A chemical equation represents a chemical reaction. It shows the reactants substances that start a reaction and products substances formed by the reaction. However, this equation isn't balanced because the number of atoms for each element is not the same on both sides of the equation. A balanced equation obeys the Law of Conservation of Mass, which states that matter is neither created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction. This is the most straightforward method.
Al cuso4 reaction
In association with Nuffield Foundation. Try this class practical or demonstration to illustrate the displacement of copper from copper II sulfate using aluminium foil. In this experiment, students add aluminium cooking foil to copper II sulfate solution and observe no reaction. They then add and dissolve sodium chloride, producing a vigorous displacement reaction which illustrates the reactivity of aluminium. The solution gets very hot, the aluminium dissolves and red copper becomes visible. The class practical can take about 30 minutes to complete. A flexicam would work well if this is to be done as a demonstration and allow students a clearer view of what is going on. The equipment required for illustrating the reaction between copper II sulfate and aluminium, before sodium chloride is added to disrupt the oxide layer on the aluminium foil. Aluminium does not show its true reactivity until the oxide layer is disturbed. Sodum chloride disturbs this oxide layer. Scratches on the surface of the oxide layer allow chloride ions to react with aluminium, this effects the cohesiveness of the oxide layer. This allows reaction with the copper II sulfate. Remind students what copper looks like, so that they know what they are looking for. Use a related experiment from our Exhibition Chemistry series to demonstrate the reactivity of aluminium using hydrochloric acid and mercury. How pure is paracetamol?
Chemistry tools. Try this demonstration Use a related experiment from our Exhibition Chemistry series to demonstrate the reactivity of aluminium using al cuso4 reaction acid and mercury. If you do not know what products are, enter reagents only and click 'Balance'.
.
Direct link to this balanced equation:. A chemical equation represents a chemical reaction. It shows the reactants substances that start a reaction and products substances formed by the reaction. However, this equation isn't balanced because the number of atoms for each element is not the same on both sides of the equation. A balanced equation obeys the Law of Conservation of Mass, which states that matter is neither created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction. This is the most straightforward method. It involves looking at the equation and adjusting the coefficients to get the same number of each type of atom on both sides of the equation.
Al cuso4 reaction
In association with Nuffield Foundation. Try this class practical or demonstration to illustrate the displacement of copper from copper II sulfate using aluminium foil. In this experiment, students add aluminium cooking foil to copper II sulfate solution and observe no reaction. They then add and dissolve sodium chloride, producing a vigorous displacement reaction which illustrates the reactivity of aluminium. The solution gets very hot, the aluminium dissolves and red copper becomes visible. The class practical can take about 30 minutes to complete. A flexicam would work well if this is to be done as a demonstration and allow students a clearer view of what is going on. The equipment required for illustrating the reaction between copper II sulfate and aluminium, before sodium chloride is added to disrupt the oxide layer on the aluminium foil. Aluminium does not show its true reactivity until the oxide layer is disturbed. Sodum chloride disturbs this oxide layer.
Dharma & greg
The equation is balanced. Best for: Equations that are more complex and not easily balanced by inspection. However, this equation isn't balanced because the number of atoms for each element is not the same on both sides of the equation. However, this equation isn't balanced because the number of atoms for each element is not the same on both sides of the equation. Enter a chemical equation to balance:. Best for: Simple equations with a small number of atoms. Each molecule's coefficient is represented by a variable like x, y, z , and a series of equations are set up based on the number of each type of atom. Best For: Redox reactions where electron transfer occurs. A chemical equation represents a chemical reaction. Site powered by Webvision Cloud.
.
Sign in Register. The solution gets very hot, the aluminium dissolves and red copper becomes visible. Balance the changes using electrons: Multiply the number of calcium atoms by 3 and the number of phosphorus atoms by 2. Useful for redox reactions, this method involves balancing the equation based on the change in oxidation numbers. Process: Start with the most complex molecule or the one with the most elements, and adjust the coefficients of the reactants and products until the equation is balanced. Balancing with inspection or trial and error method This is the most straightforward method. In this activity you investigate the purity and identity of your laboratory prepared samples of nitrophenol or paracetamol using thin-layer chromatography. By using this website, you signify your acceptance of Terms and Conditions and Privacy Policy. Each molecule's coefficient is represented by a variable like x, y, z , and a series of equations are set up based on the number of each type of atom. You're not signed in. Useful for redox reactions, this method involves balancing the equation based on the change in oxidation numbers.

0 thoughts on “Al cuso4 reaction”