Air ratio sensor
Vehicle manufacturers face many challenges when producing automobiles. One of the greatest is balancing the consumer's desire for high performance with the government's mandate to keep the air clean. The demands on engineers to reduce tailpipe emissions, increase fuel economy and improve engine performance drive the creation of many new technologies, air ratio sensor.
Published on December 21st, Innova diagnostic scanners assist you in understanding your vehicle, finding problems, and providing guidance for repairs. You can access the same advanced technology used by professionals, without the high costs or subscription fees. Air-fuel ratio is a critical parameter in combustion engines as it determines the efficiency and performance of the engine. The proper balance between air and fuel ensures optimal combustion, leading to maximum power output and minimal emissions. It measures the oxygen content in the exhaust gases and provides feedback to the Engine Control Module ECM to adjust the fuel injection for optimal combustion.
Air ratio sensor
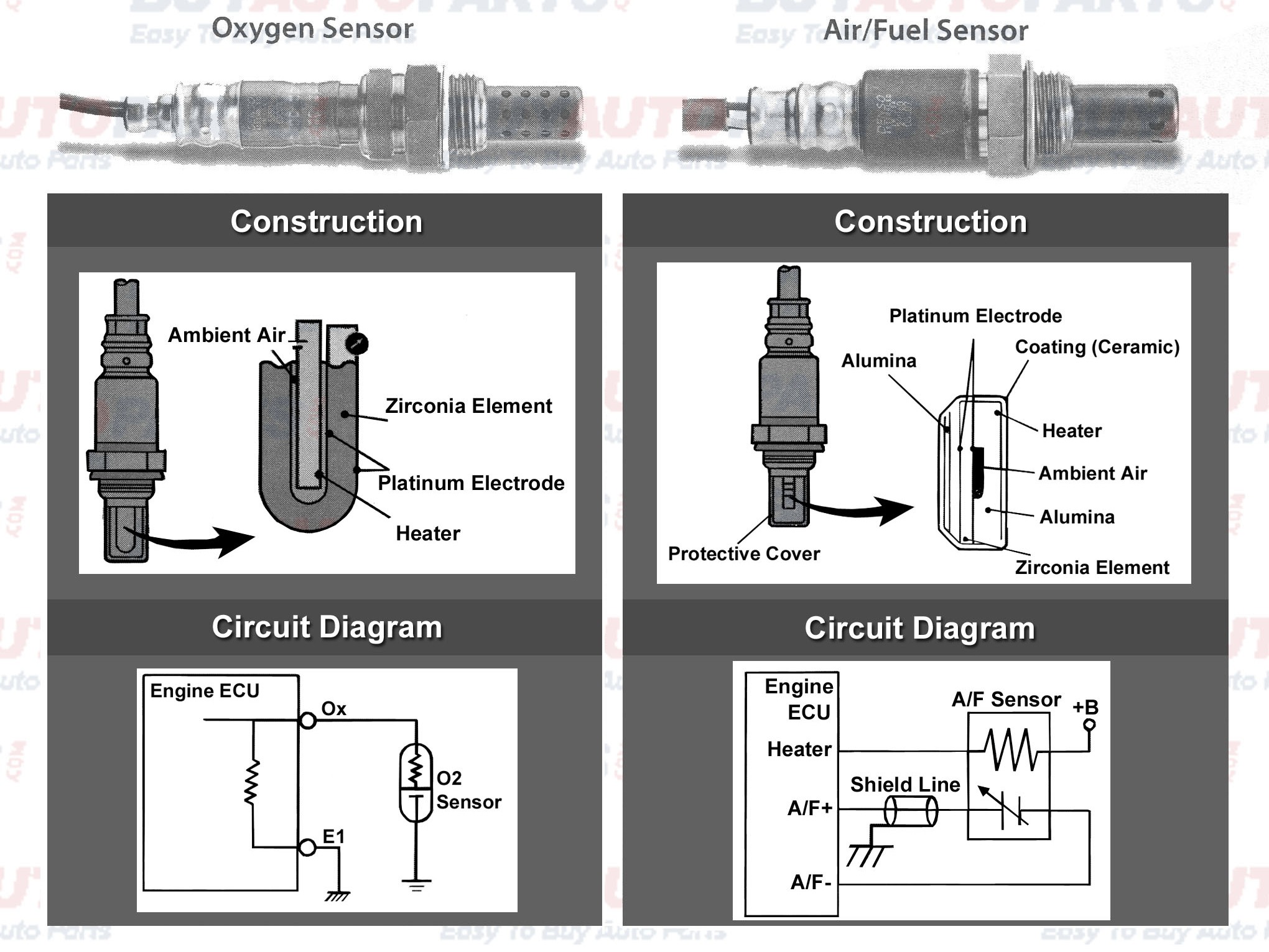
An air-fuel ratio meter monitors the air—fuel ratio of an internal combustion engine. Also called air—fuel ratio gauge , air—fuel meter , or air—fuel gauge , it reads the voltage output of an oxygen sensor , sometimes also called AFR sensor or lambda sensor. The original narrow-band oxygen sensors became factory installed standard in the late s and early s. In recent years a newer and much more accurate wide-band sensor, though more expensive, has become available. Most stand-alone narrow-band meters have 10 LEDs and some have more. These usually have 10 or 20 LEDs. Analogue 'needle' style gauges are also available. As stated above, there are wide-band meters that stand alone or are mounted in housings. Nearly all of these show the air—fuel ratio on a numeric display since the wide-band sensors provide a much more accurate reading. As wide-band sensors use more accurate electronics, these meters are more expensive. Lean mixtures improve the fuel economy but also cause sharp rises in the amount of nitrogen oxides NOX. If the mixture becomes too lean, the engine may fail to ignite, causing misfire and a large increase in unburned hydrocarbon HC emissions.
The pump cell then discharges the excess oxygen through the diffusion gap by means of the current created in air ratio sensor pump-cell circuit. These sensors are limited in their ability to accurately measure air-fuel ratios outside the stoichiometric range. Download as PDF Printable version.
To comply with current and future emissions targets, engine management technology never rests, as leading original equipment OE component manufacturers such as DENSO, continue to develop more sophisticated sensors to satisfy the needs of the VMs. This provides a greater degree of control over the combustion process, and as a result, the efficiency of the catalytic converter can be improved significantly. Also, in case of a cold start, the engine can reach a closed loop control much quicker, which reduces the emission of unburned hydrocarbons. It goes without saying that the signals that these two types of sensors produce are very different from each other, therefore, they cannot be exchanged. Despite the rise in popularity of pure electric powertrains, vehicle manufacturers VMs are still under intense pressure to improve the ecological performance of their combustion engines to comply with evermore strict emissions targets. The cut-sensor picture.
As an Amazon associate, we earn from qualifying purchases. Published on December 21st, Innova diagnostic scanners assist you in understanding your vehicle, finding problems, and providing guidance for repairs. You can access the same advanced technology used by professionals, without the high costs or subscription fees. Air-fuel ratio is a critical parameter in combustion engines as it determines the efficiency and performance of the engine. The proper balance between air and fuel ensures optimal combustion, leading to maximum power output and minimal emissions. It measures the oxygen content in the exhaust gases and provides feedback to the Engine Control Module ECM to adjust the fuel injection for optimal combustion. The primary purpose of the AFR sensor is to monitor oxygen density in the exhaust gas and provide the information to the ECM. The ECM uses this information to adjust the amount of fuel in the air-fuel mixture. By constantly analyzing the oxygen level in the exhaust gases, the sensor enables the ECM to adjust the fuel delivery, ensuring the engine operates at the ideal air-fuel ratio for optimal performance and emission control.
Air ratio sensor
You certainly can't test amperage with them using a lab scope. So let's go through a little bit of a description of how they work and then we'll go through the scanner and see how to test them. Let's get into some information about how they worked first. So we'll go in there Guided Component Tests menu , it's in the fuel injection system and there it is. And the first thing is always component information once we open a component. So we'll go in there and see how it works. The sensor contains a pumping cell and a reference cell separated by a porous diffusion gap. So basically it's like two oxygen sensors together in a sandwich.
Valencia spain weather
Under lean conditions such as deceleration the voltage should increase. The voltage typically should be 2. In this case, if you created a lean condition with a vacuum leak, the voltage would increase to approximately. Hit space bar to expand submenu Products. Instead of generating its own voltage, the titanium O 2 sensor's electrical resistance changes according to the exhaust oxygen content. The sensor will function like a conventional O 2 sensor, ranging in voltage from 0 to 1. The primary purpose of the AFR sensor is to monitor oxygen density in the exhaust gas and provide the information to the ECM. For this reason, the easiest but not the only way to test an AFR sensor is with the scanner. With their ability to measure air-fuel ratios across a wide range, these sensors contribute to improved engine performance, fuel efficiency, and reduced emissions, making them essential components in today's automotive industry. The air-fuel ratio is the ratio of the mass of air to the mass of fuel in the combustion mixture.
Log in. Sign up.
In either case, if the sensor does not respond, it likely has a problem. You'd expect the sensor to sweep up and down a range of 0 to 1. But one change that was made was the addition of a sensor heater. As with the zirconia sensor, the titanium O 2 sensor is also considered a narrow-band O 2 sensor. Learn more about our OBD2 scanners and how it can help diagnose the hidden issues with your vehicle. Digital Multimeters. Like Reddit but for automotive lovers. Such control is needed on new lean burning engines with extremely low emission output levels. The ideal stoichiometric ratio is the chemically correct ratio of air and fuel that allows for complete combustion without any excess air or fuel. Scanner Support. Enter email address Join.

I am final, I am sorry, but I suggest to go another by.