Aerosol optical thickness
This post contains formulas!
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript. An Author Correction to this article was published on 04 December Aerosol optical depth AOD is one of essential atmosphere parameters for climate change assessment as well as for total ecological situation study. Atmospheric aerosol is the most common in natural conditions type of disperse system, consisting of solid and liquid particles, suspended in the atmosphere.
Aerosol optical thickness
In physics , optical depth or optical thickness is the natural logarithm of the ratio of incident to transmitted radiant power through a material. Thus, the larger the optical depth, the smaller the amount of transmitted radiant power through the material. Spectral optical depth or spectral optical thickness is the natural logarithm of the ratio of incident to transmitted spectral radiant power through a material. The use of the term "optical density" for optical depth is discouraged. In chemistry , a closely related quantity called " absorbance " or "decadic absorbance" is used instead of optical depth: the common logarithm of the ratio of incident to transmitted radiant power through a material, that is the optical depth divided by ln Optical depth measures the attenuation of the transmitted radiant power in a material. Attenuation can be caused by absorption, but also reflection, scattering, and other physical processes. In atomic physics , the spectral optical depth of a cloud of atoms can be calculated from the quantum-mechanical properties of the atoms. In atmospheric sciences , one often refers to the optical depth of the atmosphere as corresponding to the vertical path from Earth's surface to outer space; at other times the optical path is from the observer's altitude to outer space. The optical depth of the atmosphere can be measured with a Sun photometer. This means that each photon emitted at the photosphere suffers an average of less than one scattering before it reaches the observer. Note that the optical depth of a given medium will be different for different colors wavelengths of light. For planetary rings , the optical depth is the negative logarithm of the proportion of light blocked by the ring when it lies between the source and the observer.
The Tarim Basin and the Gobi Desert are one of the primary sources of dust not only in China, but in all Asian region. Wang, Y. Show Aerosol optical thickness Maps.
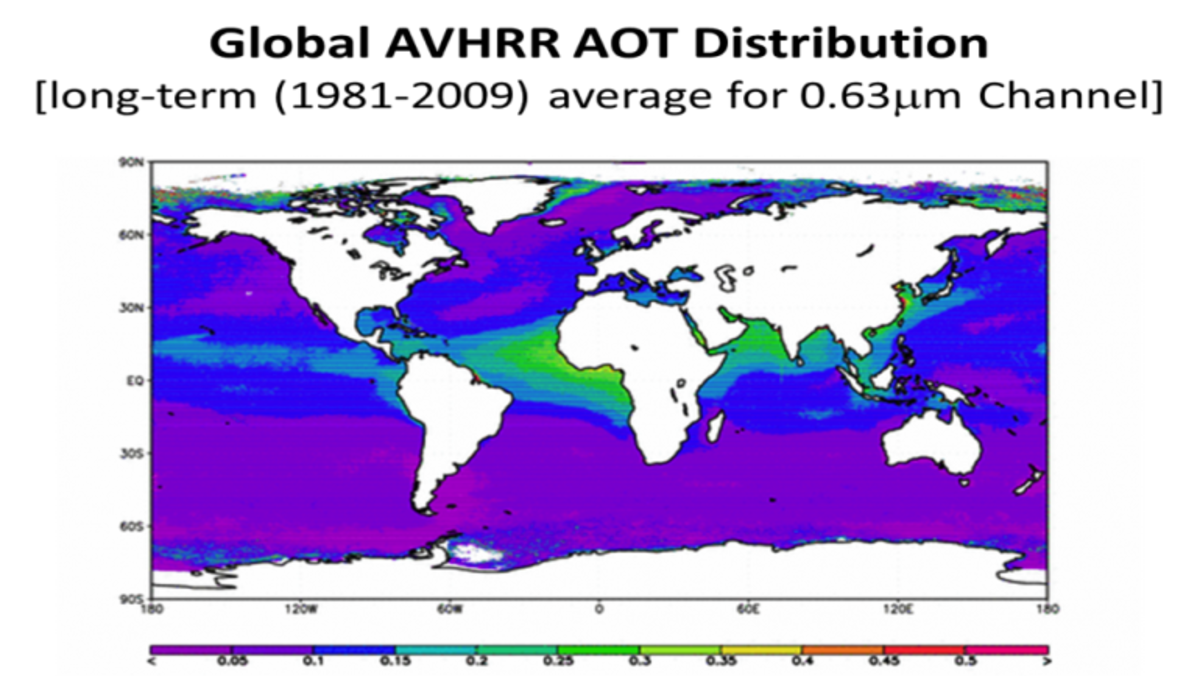
Tiny solid and liquid particles suspended in the atmosphere are called aerosols. Windblown dust, sea salts, volcanic ash, smoke from wildfires, and pollution from factories are all examples of aerosols. Depending upon their size, type, and location, aerosols can either cool the surface, or warm it. They can help clouds to form, or they can inhibit cloud formation. And if inhaled, some aerosols can be harmful to people's health. Satellite measurements of aerosols, called aerosol optical thickness, are based on the fact that the particles change the way the atmosphere reflects and absorbs visible and infrared light.
The aerosol quantity determined by most instruments is the aerosol optical depth AOD. This is related to the amount of light aerosols scatter or absorb in a column through the atmosphere specifically, it is the vertically-integrated aerosol extinction , and is also sometimes referred to as aerosol optical thickness AOT. AOD depends on wavelength; a common reference wavelength reported by satellite data products is nm. This is related to the aerosol particle size. Roughly speaking , values less than 1 suggest an optical dominance of coarse particles e.
Aerosol optical thickness
Tiny solid and liquid particles suspended in the atmosphere are called aerosols. Windblown dust, sea salts, volcanic ash, smoke from wildfires, and pollution from factories are all examples of aerosols. Depending upon their size, type, and location, aerosols can either cool the surface, or warm it.
Yes daddy meme
Levy, H. Main article: Optical depth astrophysics. Main article: Attenuation. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. Unfortunately, to correct the effects of aerosols, there is no global aerosol observation network, and the only available data are local observations from the few hundred points of Aeronet network. ISBN All authors reviewed the manuscript. Seasonal variations in aerosol optical properties over China. The abundance variations result in great variations of observable reflectances from one day to the next, and it is therefore necessary to know the quantity and type of aerosols, in order to correct their effects. Online corrected version: — " Absorbance ". In spring the whole territory of the country is exposed to dust, which comes from the territories of North and Northwest China, leading to increase of AOD. Show All Maps. Due to low amount of precipitations and relatively high wind speeds these regions are subject to soil erosion. Download citation. Email address Sign up.
In the maps shown here, dark brown pixels show high aerosol concentrations, while tan pixels show lower concentrations, and light yellow areas show little or no aerosols.
So, there is no need to apply atmospheric correction over the ocean. Levy, H. Xie, Y. Kang, N. This enables to use MODIS data to perform various tasks on regular monitoring of natural phenomena within a large region. Seasonal AOD variation is characterized by two distribution peaks - in spring and in autumn with predominance of coarse particles in the total concentration of aerosol particles. Industrialization and urbanization process, which for the last thirty years has been peculiar to all territory of the country, is characterized by consumption of enormous amount of fossil fuel coal, oil , which results in emission of a significant amount of anthropogenic secondary aerosols 62 , 63 , Intercomparison between satellite-derived aerosol optical thickness and PM2. This data can be used to teach or learn the following topics and skills in introductory Earth science:. Optical depth measures the attenuation of the transmitted radiant power in a material. Ma, Y. Sundog Pub. The investigations covered the most rapidly developing regions of the country, such as the Yangtze River Delta 39 , 40 , the Pearl River Delta 41 , 42 , the North China Plain 20 , 43 and the Sichuan Basin 44 , Although in summer the amount of precipitation in this region increases, but at high temperature and humidity we observe acceleration of gas transformation into particles and hygroscopic growth of aerosol particles 14 , 42 , 64 , Google Scholar Wang, L.

What excellent words