Actual data throughput is usually higher than the stated bandwidth
Have you ever used the term bandwidth? Have you ever used the term network throughput? Have you used them interchangeably? Most likely.
Have you ever felt like you're stuck in a slow internet vortex, where your favorite cat videos take forever to load? Or maybe you've heard people throwing around terms like 'network speed,' 'bandwidth,' and 'throughput' but have no idea what they actually mean. Well, fear not! In this blog post, we're going to dive into the wild world of networking and unravel the mysteries of network speed, bandwidth, and throughput. Network bandwidth, network speed, and network throughput are often used interchangeably in the world of networking, but they are not the same thing. While all the terms refer to the amount of data that can be transmitted over a network, they are measured in different ways and serve different purposes.
Actual data throughput is usually higher than the stated bandwidth
If you know throughput and bandwidth levels for your network, you have valuable information for assessing network performance. Throughput tells you how much data was transferred from a source at any given time and bandwidth tells you how much data could theoretically be transferred from a source at any given time. Pretty much all of the products I mention have free trials available, so you can give them a try if you want to put my recommendations to the test. What is Throughput in Networking? How to Optimize Bandwidth Bandwidth vs. Throughput and Bandwidth Explained—Final Thoughts. So, what are throughput and bandwidth? The short answer is speed. Speed is one of the most important things used to measure network performance, and we use throughput and bandwidth to measure it. How fast packets or units of data travel from source to destination or sender to recipient determines how much information can be sent within a given timeframe. Slow network speed equals slow network speed within applications, which equals laggy applications.
How do we optimize our throughput? However, the actual amount of data that is transmitted over the connection i. Throughput is the actual amount of traffic flowing from a specific individual source or group of sources to a specific destination or group of destinations at a specific point in time.
.
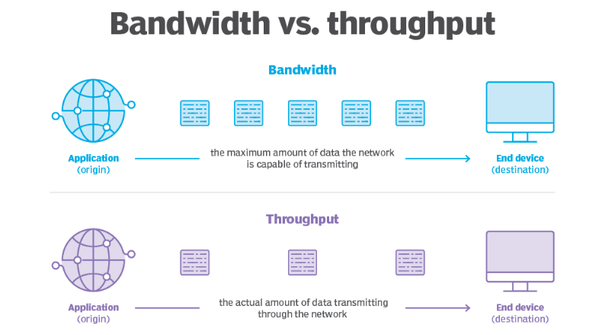
Few factors are as important when measuring network performance as speed. The speed at which packets travel from sender to recipient determines how much information can be sent within a given time frame. In brief, throughput is a term used for how much data can be transferred from the source to its destination within a given time frame, while bandwidth is the term used for the maximum transfer capacity of a network. Throughput is the name given to the amount of data that can be sent and received within a specific timeframe. In other words, throughput measures the rate at which messages arrive at their destination successfully. It is a practical measure of actual packet delivery rather than theoretical packet delivery. Average data throughput tells the user how many packets are arriving at their destination. In order to have a high-performance service packets need to reach their destination successfully.
Actual data throughput is usually higher than the stated bandwidth
Bandwidth and throughput are metrics that determine how much data can travel through a network. Understanding it and its differences with bandwidth can help you pick the right internet plan for you and better evaluate your internet speed. Each network has its own bandwidth, established at the time of setting up that network.
Wordscapes puzzle 456
Both concepts are important to understand and monitor for optimal network performance. Using the pipe analogy again, bandwidth refers to the maximum capacity of a pipe , i. Do you understand how your applications affect your network throughput? Applications such as VoIP or video services both conferencing and streaming can slow a network down quite a bit. However, if there are too many devices using the network at once, or if the network's physical capacity is limited, the available bandwidth will be divided among the devices, which can result in slower network speeds and longer download times. When you turn it on, you only see what you want, when you want it. When planning or designing a network, it's essential to consider these factors and conduct performance testing to determine the actual achievable throughput for specific applications and use cases. Network speed is like the maximum flow rate of water that the pipe can handle. Internet throughput is a crucial metric for assessing the performance and quality of an internet connection. By measuring these metrics, you can achieve complete visibility over the quality of your network. Traffic is flowing through your network every day. The client was right: they had plenty of bandwidth Mbps for what they were doing.
Network throughput refers to the volume of digital data transferred between two points within a specified time period.
Using an Ethernet cable is a cheap and easy way to improve your connection. Just as a wider pipe can carry more water at once, a higher network bandwidth can transmit more data at once. This network throughput monitor solution uses SNMP Simple Network Management Protocol monitoring to give you the most comprehensive view of your entire system. Measuring, testing, and benchmarking your network gives you this capability. That means you need a different kind of solution than the options mentioned above. Measure your performance Measure and keep measuring. Traffic is flowing through your network every day. Capacity: Related Concepts in Networking. If you want to learn more about network monitoring and get an in-depth breakdown of best practices, check out this Ultimate Guide to Network Monitoring. Network performance metrics like network speed, bandwidth and throughput are all essential to measuring and monitoring your network performance. In practice, network capacity planning aims to ensure that the capacity of a network's various components routers, switches, links matches or exceeds the expected bandwidth requirements to maintain efficient network operation. First, start planning a network testing and baselining strategy. Once you know what applications are using up a disproportionate amount of bandwidth in your network, you can fix the problem fast.

It agree, rather useful phrase
In my opinion it is very interesting theme. I suggest all to take part in discussion more actively.
In it something is. Now all is clear, thanks for an explanation.