50s ribosomal subunit
Thank you for visiting 50s ribosomal subunit. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
The structures of ribosomal proteins and their interactions with RNA have been examined in the refined crystal structure of the Haloarcula marismortui large ribosomal subunit. The protein structures fall into six groups based on their topology. The 50S subunit proteins function primarily to stabilize inter-domain interactions that are necessary to maintain the subunit's structural integrity. An extraordinary variety of protein-RNA interactions is observed. Electrostatic interactions between numerous arginine and lysine residues, particularly those in tail extensions, and the phosphate groups of the RNA backbone mediate many protein-RNA contacts.
50s ribosomal subunit
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Despite the identification of many factors that facilitate ribosome assembly, the molecular mechanisms by which they drive ribosome biogenesis are poorly understood. Here, we analyze the late stages of assembly of the 50S subunit using Bacillus subtilis cells depleted of RbgA, a highly conserved GTPase. We found that RbgA-depleted cells accumulate late assembly intermediates bearing sub-stoichiometric quantities of ribosomal proteins L16, L27, L28, L33a, L35 and L Cryo-electron microscopy and chemical probing revealed that the central protuberance, the GTPase associating region and tRNA-binding sites in this intermediate are unstructured. These findings demonstrate that key functional sites of the 50S subunit remain unstructured until late stages of maturation, preventing the incomplete subunit from prematurely engaging in translation. Finally, structural and biochemical analysis of a ribosome particle depleted of L16 indicate that L16 binding is necessary for the stimulation of RbgA GTPase activity and, in turn, release of this co-factor, and for conversion of the intermediate to a complete 50S subunit. In bacteria, ribosome biogenesis requires the synthesis, folding, chemical modification and assembly of 3 large RNAs and 55 proteins. This complex process is completed rapidly and efficiently with bacterial cells synthesizing up to 50 ribosomes per generation 1.
In addition, the yeast homolog of L16, Rpl10p, is one of the last r-proteins to be incorporated into the 60S subunit and its binding is controlled by the RbgA 50s ribosomal subunit Lsg1p
Bacteria harbor a number GTPases that function in the assembly of the ribosome and are essential for growth. Homologs of this protein are also implicated in the assembly of the large subunit of the mitochondrial and eukaryotic ribosome. We present here the cryo-electron microscopy structure of RbgA bound to a Bacillus subtilis 50S subunit assembly intermediate 45S RbgA particle that accumulates in cells upon RbgA depletion. Binding of RbgA at the P site of the immature particle stabilizes functionally important rRNA helices in the A and P-sites, prior to the completion of the maturation process of the subunit. The structure also reveals the location of the highly conserved N-terminal end of RbgA containing the catalytic residue Histidine 9.
It is the site of inhibition for antibiotics such as macrolides , chloramphenicol , clindamycin , and the pleuromutilins. Despite having the same sedimentation rate, bacterial and archaeal ribosomes can be quite different. X-ray crystallography has yielded electron density maps allowing the structure of the 50S in Haloarcula marismortui archaeon to be determined to 2. The secondary structure of 23S is divided into six large domains, within which domain V is most important in its peptidyl transferase [3] activity. Each domain contains normal secondary structure e.
50s ribosomal subunit
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer.
Www pornhub com
Capel, M. Figure 5: The proteins in white backbone ribbons and RNAs in coloured ribbon of the factor-binding site that have been fitted to the density. While these structural changes are more subtle than those observed in the CP, these data indicates that the GAR is also malformed in this immature particle. Methods Mol. We demonstrated that the exogenous expression of rplT restored the growth of bipA -deleted strain at low temperature by partially recovering the defects in ribosomal RNA processing and ribosome assembly. Comparison with the other structures from S. Crude ribosomes were pelleted by centrifugation at g for 2 h and 25 min, and the pellet was dissolved in 1 ml of HMA 06 buffer 20 mM Tris—HCl pH 7. Our cryo-EM structure represents the first visualization of the conformational changes induced by a bacterial assembly factor in a ribosomal subunit intermediate. Ramagopal, S. Figure 1. Nucleic Acids Res. The molecular model of the mature 50S subunit PDB ID 3j9w was fitted to identify the relevant structural motifs in the difference map.
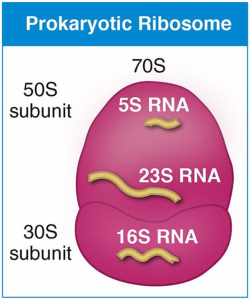
Ribosomes are composed of two subunits with densities of 50S and 30S "S" refers to a unit of density called the Svedberg unit.
The BipA B PI- i nducible p rotein A protein is highly conserved in a large variety of bacteria and belongs to the translational GTPases, based on sequential and structural similarities. Structural consequences of the interaction of RbgA with a 50S ribosomal subunit assembly intermediate. Precipitation was obtained by centrifugation at 16 g for 20 min after addition of 1 ml of subunit precipitation buffer. Reconstitution of 50S ribosomal subunits from dissociated molecular components. Table 2. Skip to main content Thank you for visiting nature. Error bars represent SD. However, these results cannot distinguish between several similar mechanistic models in which the 45S particle is competent for maturation Supplementary Figure S4B. Trends Cell Biol. The data were analyzed by unpaired two-way t -test. Acomplete mapping of the proteins in the small ribosomal subunit of E. Crude ribosomes were pelleted by centrifugation at g for 2 h and 25 min, and the pellet was dissolved in 1 ml of HMA 06 buffer 20 mM Tris—HCl pH 7.

It is draw?
Bravo, this phrase has had just by the way